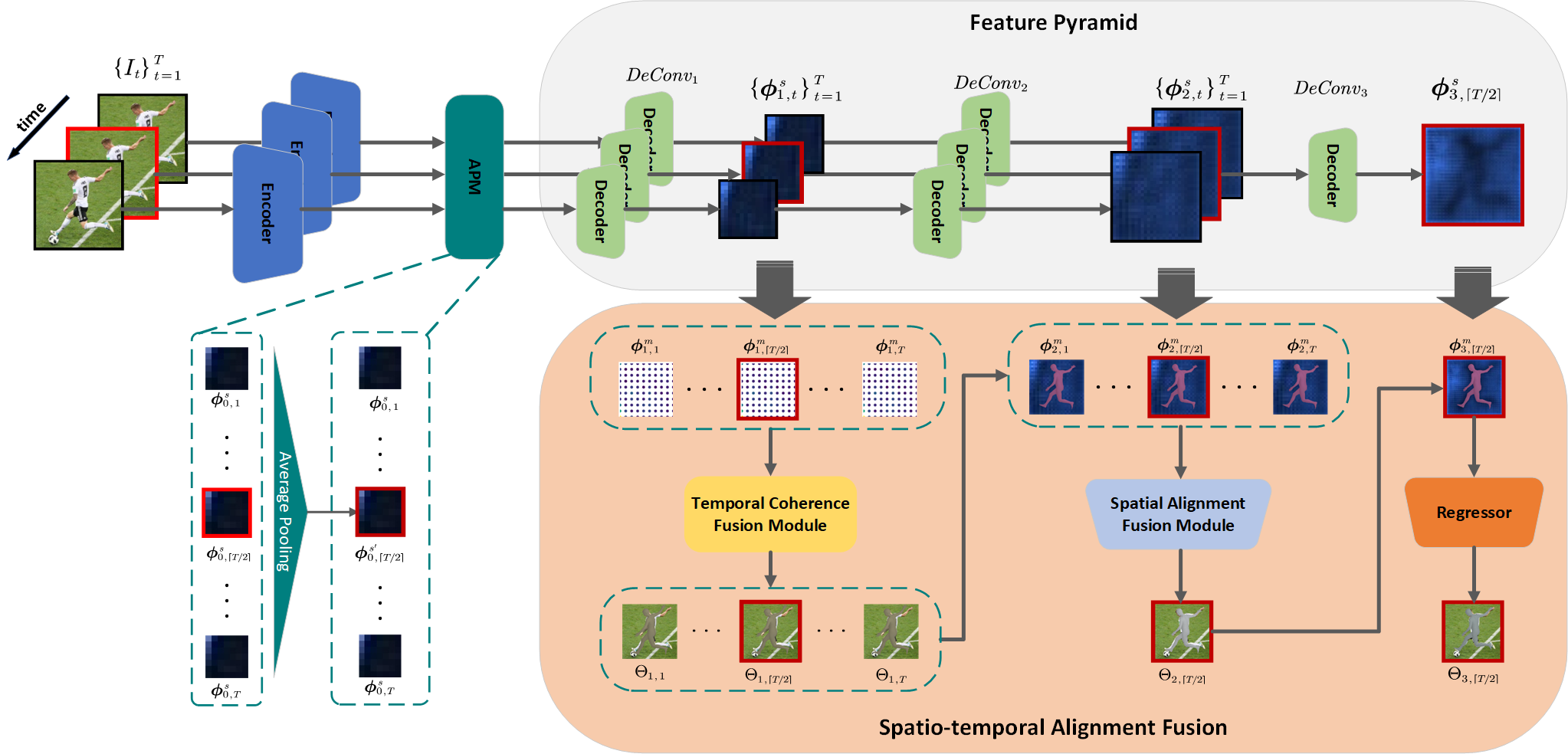
—The recovery of 3D human mesh from monocular images has significantly been developed in recent years. However, existing models usually ignore spatial and temporal information, which might lead to mesh and image misalignment and temporal discontinuity. For this reason, we propose a novel Spatio-Temporal Alignment Fusion (STAF) model. As a video-based model, it leverages coherence clues from human motion by an attention-based Temporal Coherence Fusion Module (TCFM). As for spatial mesh-alignment evidence, we extract fine-grained local information through predicted mesh projection on the feature maps. Based on the spatial features, we further introduce a multi-stage adjacent Spatial Alignment Fusion Module (SAFM) to enhance the feature representation of the target frame. In addition to the above, we propose an Average Pooling Module (APM) to allow the model to focus on the entire input sequence rather than just the target frame. This method can remarkably improve the smoothness of recovery results from video. Extensive experiments on 3DPW, MPII3D, and H36M demonstrate the superiority of STAF. We achieve a state-of-the-art trade-off between precision and smoothness. We will release relative codes after publication.
@ARTICLE{yao2024staf,
author={Yao, Wei and Zhang, Hongwen and Sun, Yunlian and Tang, Jinhui},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology},
title={STAF: 3D Human Mesh Recovery From Video With Spatio-Temporal Alignment Fusion},
year={2024},
volume={34},
number={11},
pages={10564-10577},
keywords={Hidden Markov models;Three-dimensional displays;Feature extraction;Image reconstruction;Solid modeling;Biological system modeling;Coherence;3D human mesh recovery;temporal coherence;feature pyramid;attention model},
doi={10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3410400}}
[1] W.-L. Wei, J.-C. Lin, T.-L. Liu, and H.-Y. M. Liao, “Capturing humans in motion: Temporal-attentive 3d human
pose and shape estimation from monocular video”
[2] M. Kocabas, N. Athanasiou, and M. J. Black, “Vibe: Video inference for human body pose and shape estimation”
[3] Z. Luo, S. A. Golestaneh, and K. M. Kitani, “3d human motion estimation via motion compression and
refinement”